
macOS is an operating system with super intuitive navigation, sorting, and file system organization. Even for non-tech-savvy users or users coming from a Windows environment, it’s fast and easy to get used to locating your files, folders, and apps.
In fact, macOS provides users with a lot of native functions that help users locate them using file names, dates, file types, and more. This article goes over all the ways you can find files on your MacBook.
Can’t find needed files? Go straight to data recovery section ⤵
| Method | When It’s Most Useful |
| 🕓 Scan your Recents Folder | When you’re looking for a file you recently opened or created |
| 🗃️ Browse Your Default Folders | When you haven’t customized your folders |
| 🏴 Use Terminal Commands | When you want to know the the location path of your file or folder |
| 🔎 Utilize Finder Advanced Search | When you want to use a lot of parameters for searching |
| 💡 Use Spotlight Queries | When you need to quickly narrow your search |
Table of Contents
Where Are Files Stored on Mac?
On your Mac, files are stored in different folders and directories depending on their data type. Even folders you create yourself are stored in one of the pre-made directories already on macOS. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Home – The Home directory is the primary location of your personal files and settings, as well as your key subfolders: Desktop, Documents, Downloads, Pictures, Movies, Music, Public, and Library.
- Applications Folder – This folder stores “application bundles”—essentially, the bundle of files that make up your apps. Deleting apps from this folder uninstalls them from your Mac.
- Cloud Storage Folders – If you have iCloud, Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, or other cloud storage services enabled on your Mac, they will appear as folders in Finder (usually stored in ~/Library/CloudStorage).
- Trash – Trash is a special folder on Mac that stores all deleted files and provides the functionality to recover them or delete them forever.
- System-level Folders – MacOS stores most of its system files in hidden folders in /Library or /System.
5 Methods to Search for Files and Folders On a Mac
Fortunately, there are multiple ways to find all files and folders on a Mac. Some of them require manually navigating, while others are as convenient as using hotkeys to pull up a quick search function.
If you suspect that you can’t see your files because they’re hidden, there’s an easy way to show them.
Method 1: Scan your Recents Folder
macOS makes it super easy to find files that you were recently working with or you recently created, especially if you forgot where you saved them. It’s also sorted by “Date Last Opened” so you can easily pick up work where you left off. Here’s how to use it:
Step 1. Open Finder by clicking its icon on your Dock.
![]()
Step 2. Click the “Recents” folder on the left sidebar below AirDrop and within the Favorites category.
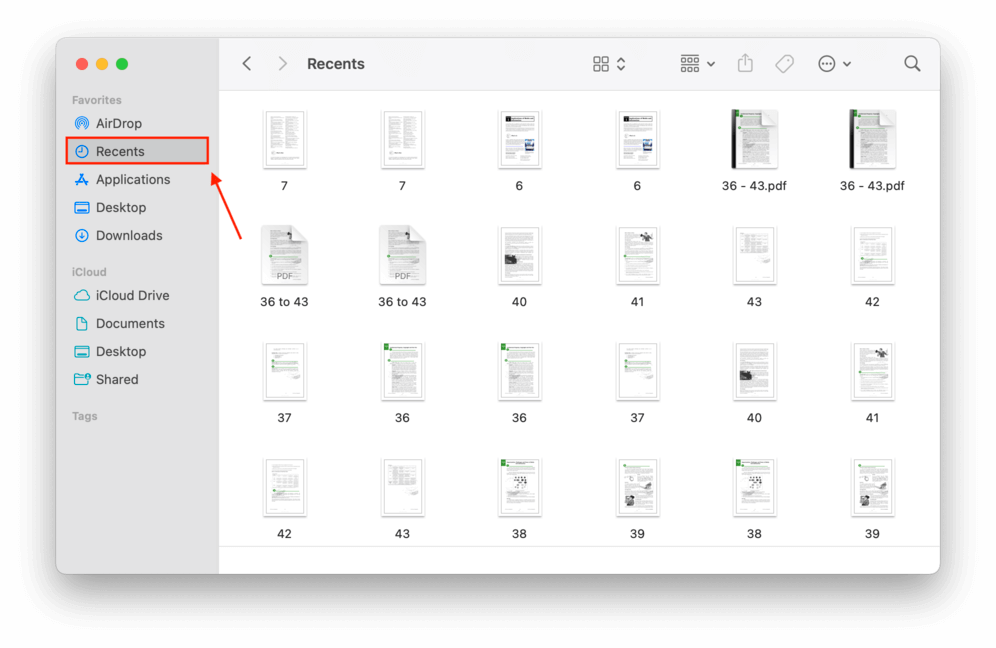
You can actually customize what folders appear in your Favorites sidebar by selecting them through Finder Preferences. Here’s how to do it:
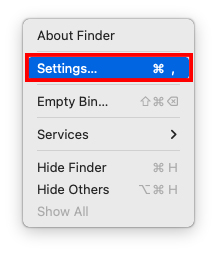
Step 1. Make sure Finder is open. Then on the Apple menu bar, click Finder > Settings.
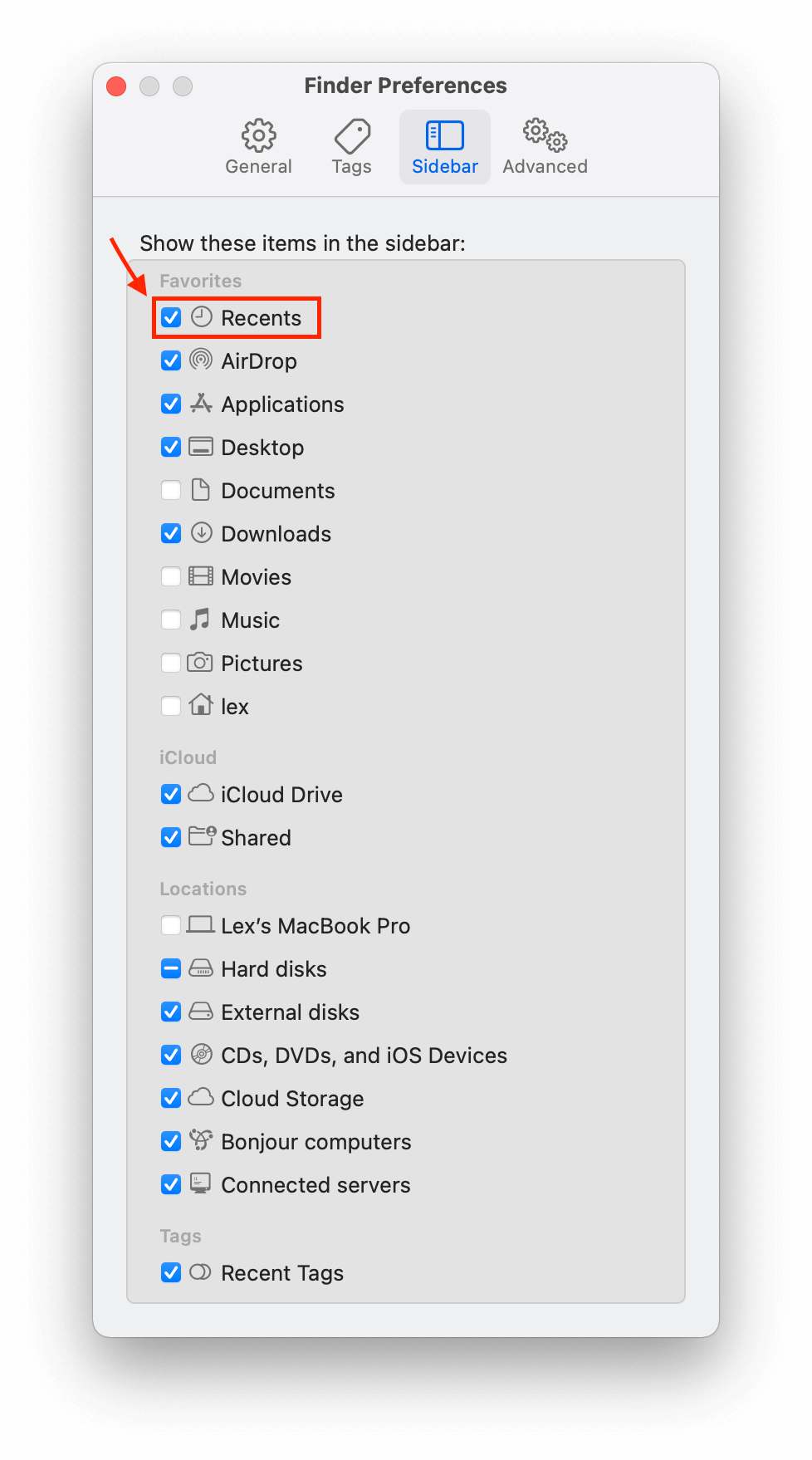
Step 2. In the Finder Preferences window, tick the box to the left of the “Recents” option.
Method 2: Browse Your Default Folders
Most files that are saved to your Mac are usually stored in one of your default folders unless you manually save them elsewhere. There are several ways to browse your default folders, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
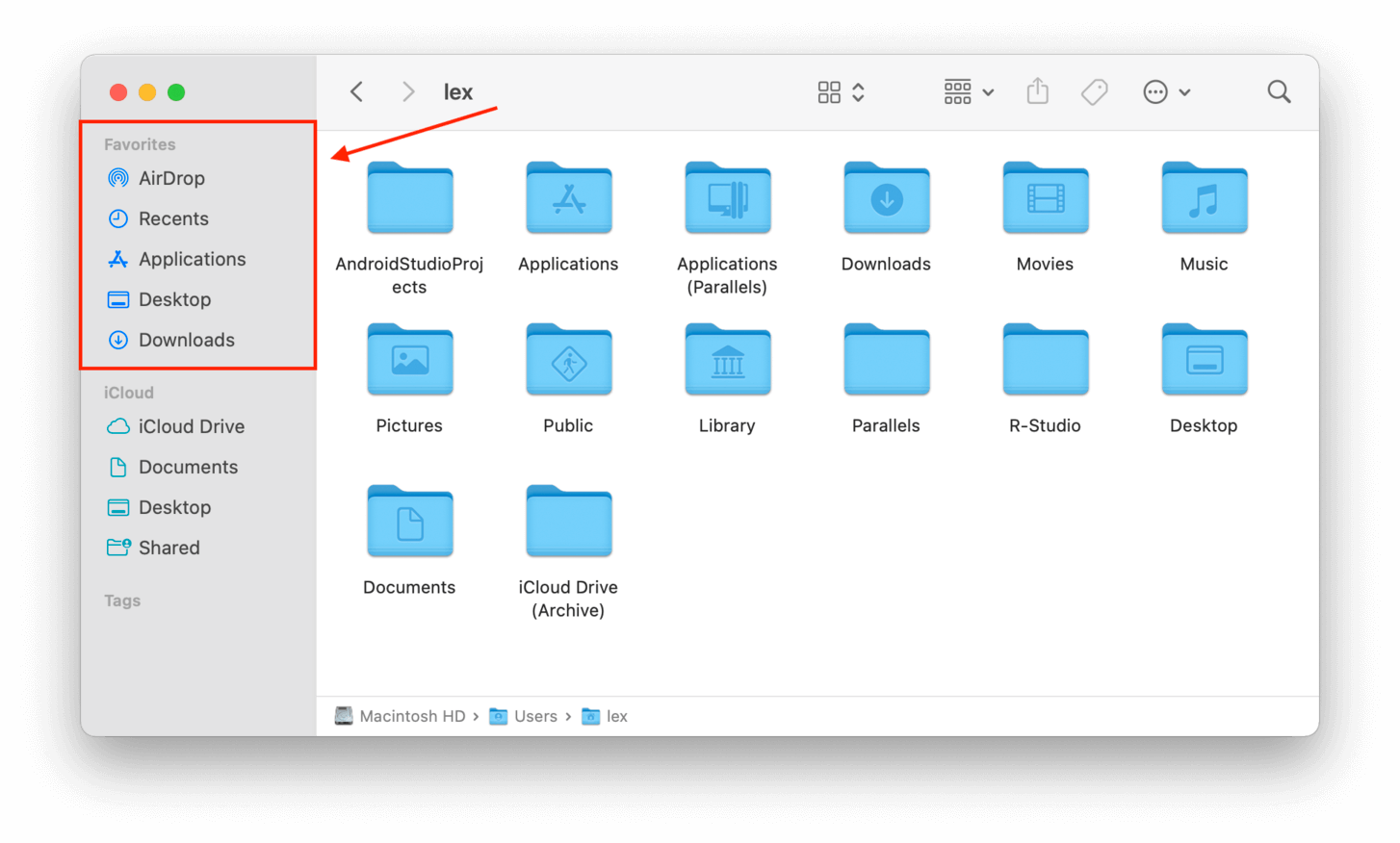
Option A: Finder Sidebar
In the Finder window, you’ll find several folders pinned to the left sidebar. The top section is your Favorites, which usually contains several often-accessed folders by default (like Recents, Desktop, and Downloads).
The bottom half is reserved for iCloud folders if you have it enabled. Then, beneath that is a section for tags so you can easily find files and folders by keyword!
Option B: Finder Go Menu
Aside from navigating through the Finder interface, you can find a more comprehensive list of directories you can jump into through the Finder > Go menu.
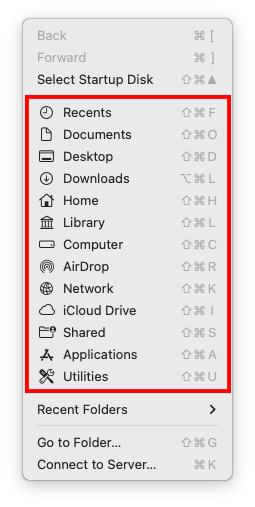
Option C: Go to Folder Function
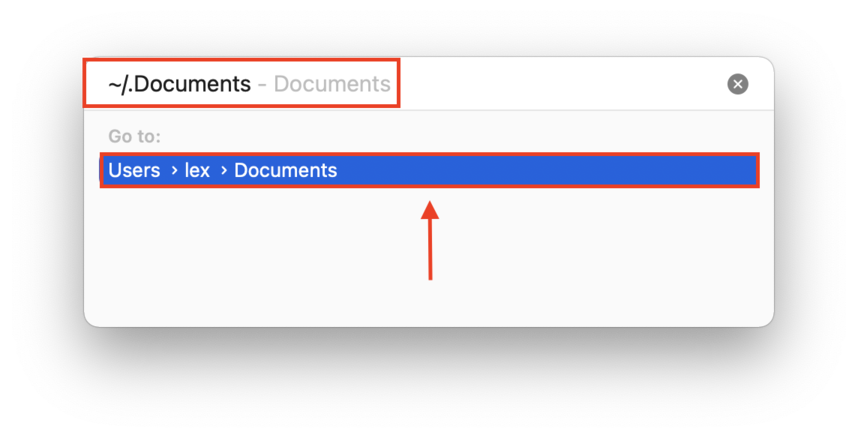
If you know the folder pathname of the directory you want to view, you can open it directly using the Go To function. This opens a search field specifically for the folders on your Mac.
Method 3: Use Terminal Commands
macOS Terminal app is a command tool that lets you access your Mac beyond what the graphical user interface shows you. We’re going to use two useful Terminal commands to folders and files on a Mac.
“find-name” Command
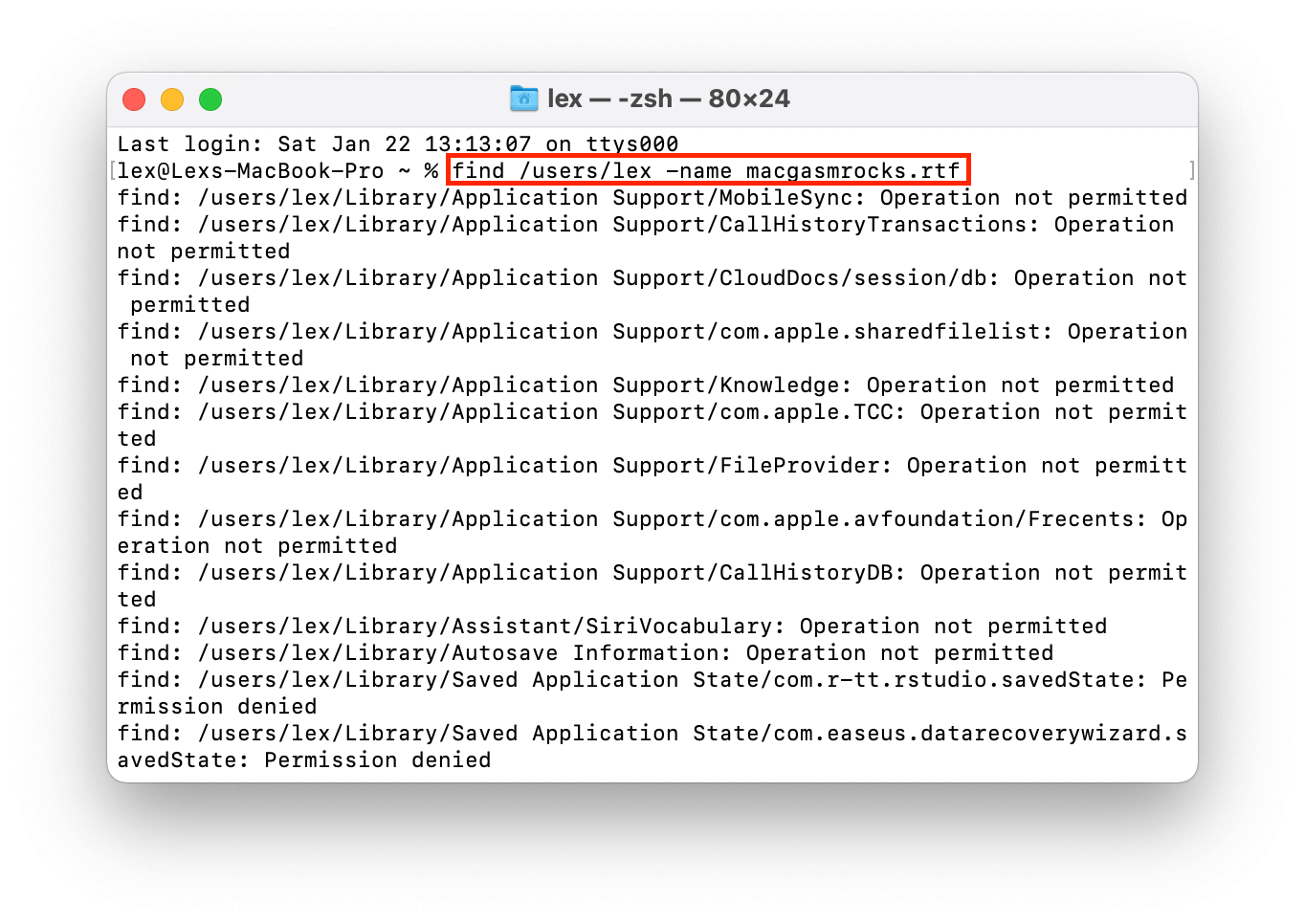
Use the “find” command to locate files in specific directories by file names. What makes this useful is that you can specify a directory further up the file structure to search through more locations. The Terminal window will then display the exact path for that file. For example, this command will search for texttxt.rtf in my entire home directory:
find /users/lex -name macgasmrocks.rtf
“mdfind” Command
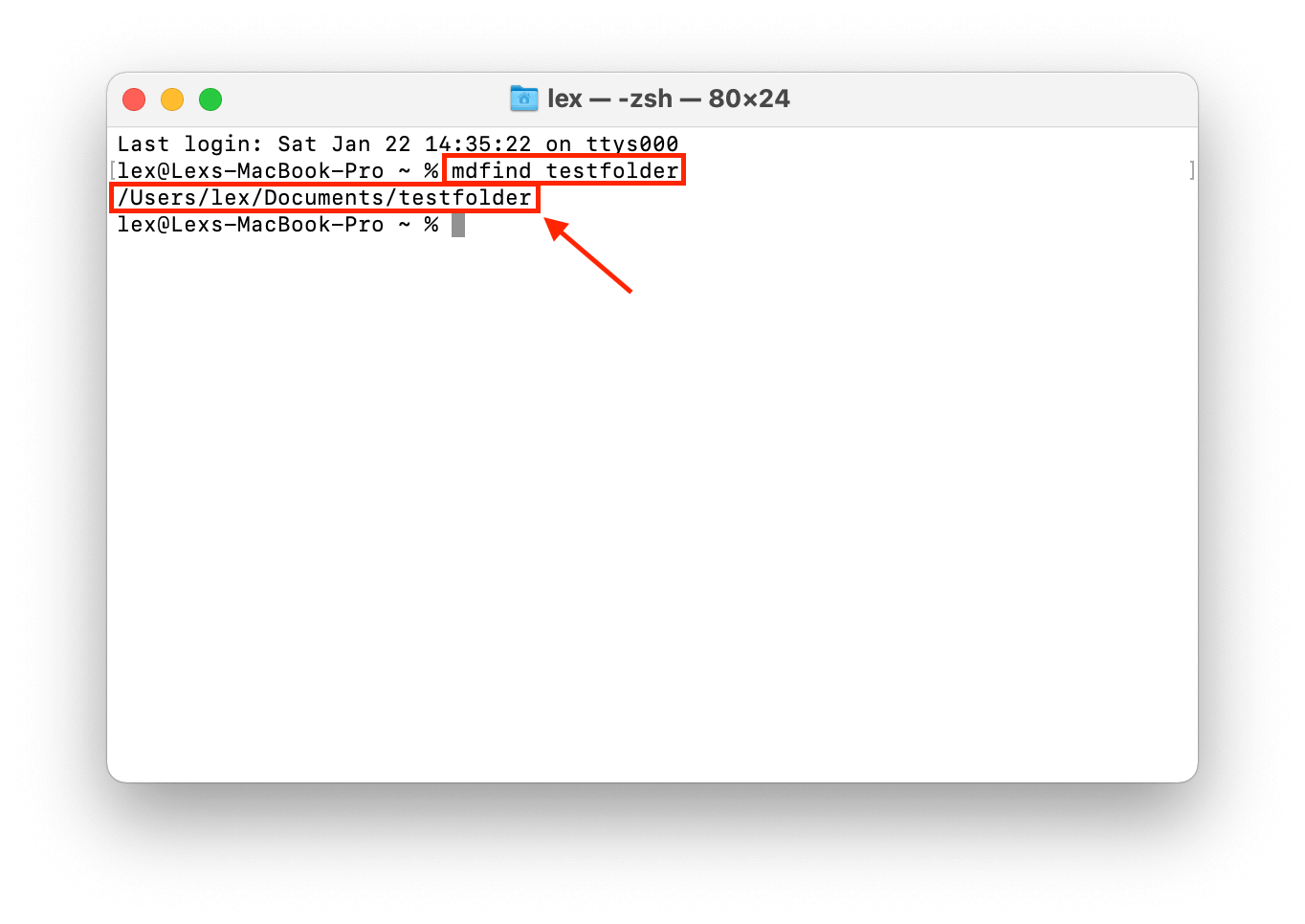
Use the “mdfind” command to search for files and folders. Like the “find” command, Terminal will help you find file and folder locations on a Mac and print the exact path. For example, let’s search for a folder:
mdfind testfolder
For files, you’ll need to include the extension in the command, such as .pdf, .jpg, etc.
Method 4: Utilize Finder Advanced Search
Finder is macOS graphical user interface organization system – Apple’s version of Windows Explorer. It’s fairly straightforward to navigate through Finder, but did you know that it also has an advanced search bar? Finder Advanced Search makes searching for files on Mac efficient. To access it, follow the steps below:
Step 1. Open Finder.
Step 2. On the menu bar, click File > Find.
![]()
Step 3. Type a query in the search field that is now highlighted in the top-right corner of the Finder window. Then, click the + button beneath the search field and use the dropdown menus that appear to specify parameters for your search. For example, you can filter files based on keywords in their file name or the date they were last opened.
You can stack as many filters as you want to narrow down the search as much as possible.
Method 5: Use Spotlight Queries
Spotlight is another intuitive native macOS function that lets you search for different types of files and apps. It’s very easy to pull up Spotlight – just press (CMD + Space). Once Spotlight is on-screen, you can proceed to try out different “queries.”
A query is a request from the user to the computer for specific data or information. Here are the most useful ones for Spotlight:
- Regular Query – A regular query means you don’t use any specific query rules
- “Name” Query – Search for a file on Mac by letters or numbers within the filename. On the Spotlight search field, type name:”string” and replace “string” with any part of your file name. For example, name:macgasmrocks.
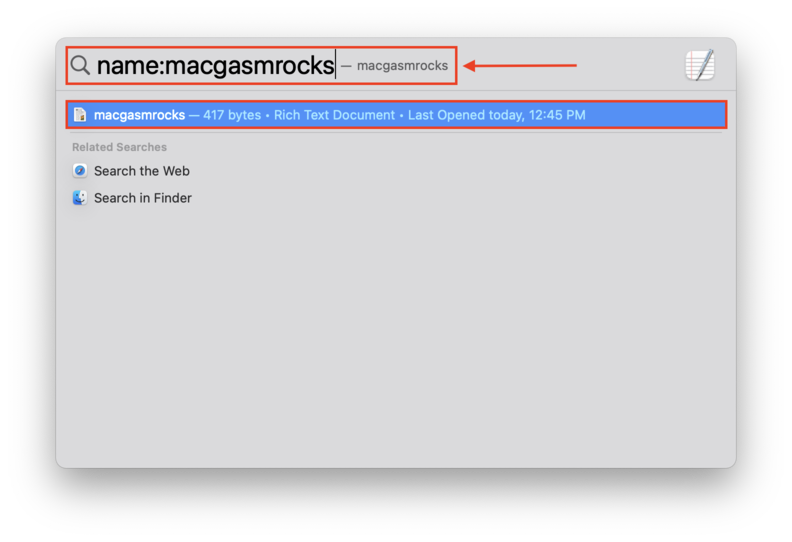
- “Kind” Query – Search files by their file type. On the Spotlight search field, type kind:”file type” and replace “file type” with the file’s type. For example, kind:pdf.
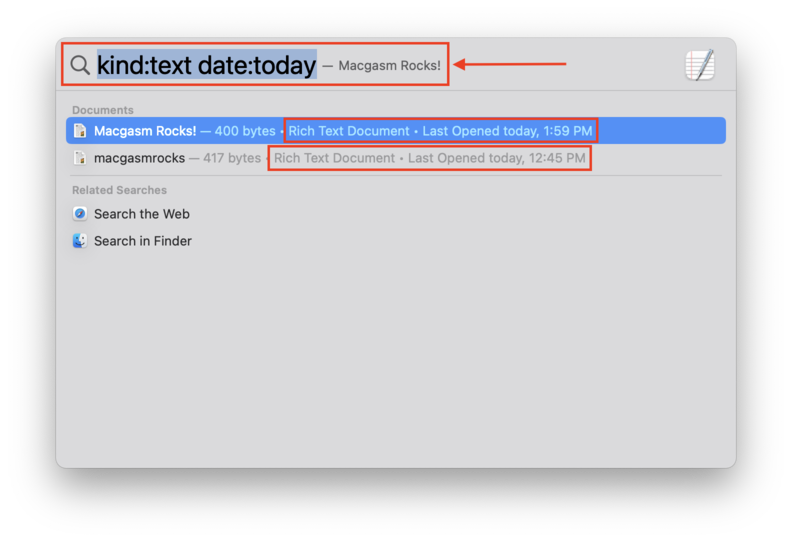
- “Date” Query – Search files and folders by the date you last opened it. On the Spotlight search field, type date:”date” and replace “date” with the date you last opened the file or folder. You can also use “today” or “yesterday.” For example: date:today.
- “Author” Query – Search for files by the author that created them. On the Spotlight search field, type author:”author name” and replace “author name” with the user who created the file.
The cool thing about Spotlight queries is that you can “stack” multiple queries to selectively narrow down your search. For example, kind:text date:today.
What To Do if You Can’t Find the Needed Files
If you’ve tried everything we discussed in this article and you still can’t find your files – or if you’ve emptied your Trash folder – then it’s likely that they were deleted by accident, by corruption, or by a nasty virus.
Below, we’ll show you the best ways to recover deleted files.
Method 1: Check Your Trash Folder
macOs’ Trash folder is the equivalent of the Windows trash bin. This is the first place to look for your recently deleted photos, documents, videos, etc. The easiest way to open it is by clicking its icon on your Dock.
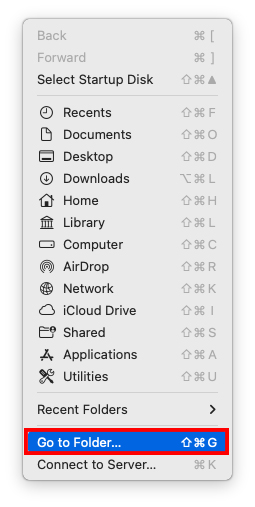
If it’s missing from your Dock for some reason, you can use the Finder “Go to folder” function. Here’s how:
Step 1. Open Finder.
Step 2. On the Apple menu bar, click Go > Go to Folder…
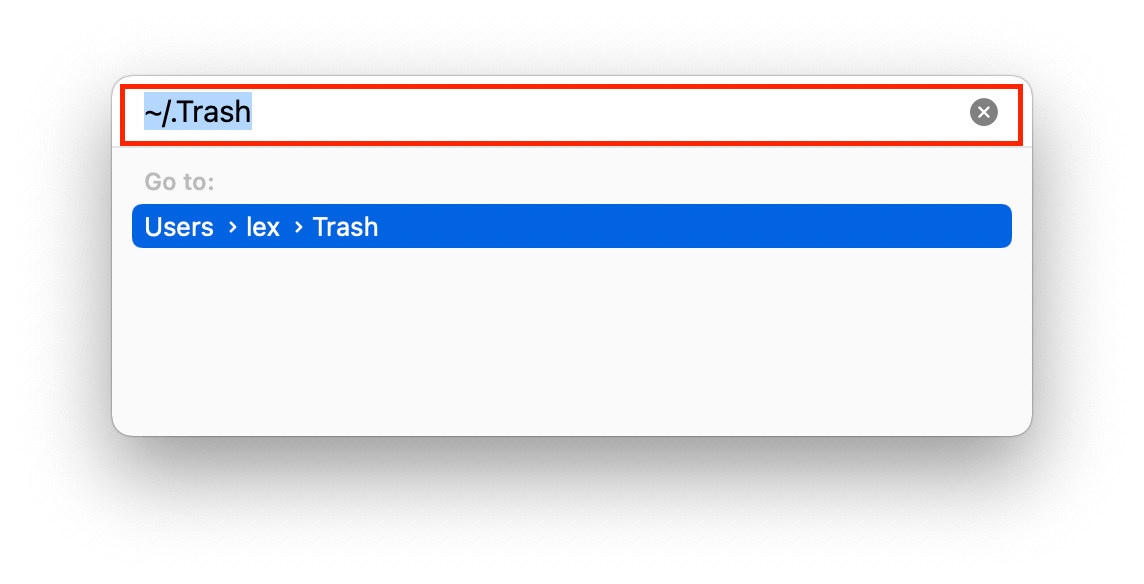
 Step 3. On the window that appears, there will be a text field. Type “~/.Trash” without the quotes, then press enter.
Step 3. On the window that appears, there will be a text field. Type “~/.Trash” without the quotes, then press enter.
If you find your files in the Trash folder, you can right-click them then click “Put Back” to return them to their original location.
Method 2: Use Data Recovery Software
If your deleted file is no longer in the Trash folder, you’ll need to use data recovery software to extract it directly from your Mac’s file system. For this article, we’ll be using Disk Drill. It’s fully optimized for the latest macOS and supports almost every single Mac-based file that exists.
It’s also easy to use, making it perfect for beginners. In the guide below, we’ll demonstrate how to use Disk Drill to restore your deleted files.
Step 1. Plug in an external storage device if you’re recovering files from your main drive.
Step 2. Download and install Disk Drill.
Step 3. Launch Disk Drill by opening Finder > Applications > Disk Drill.

Step 4. Select the drive where your missing files were last stored, and click Search for lost files to proceed with the scan.
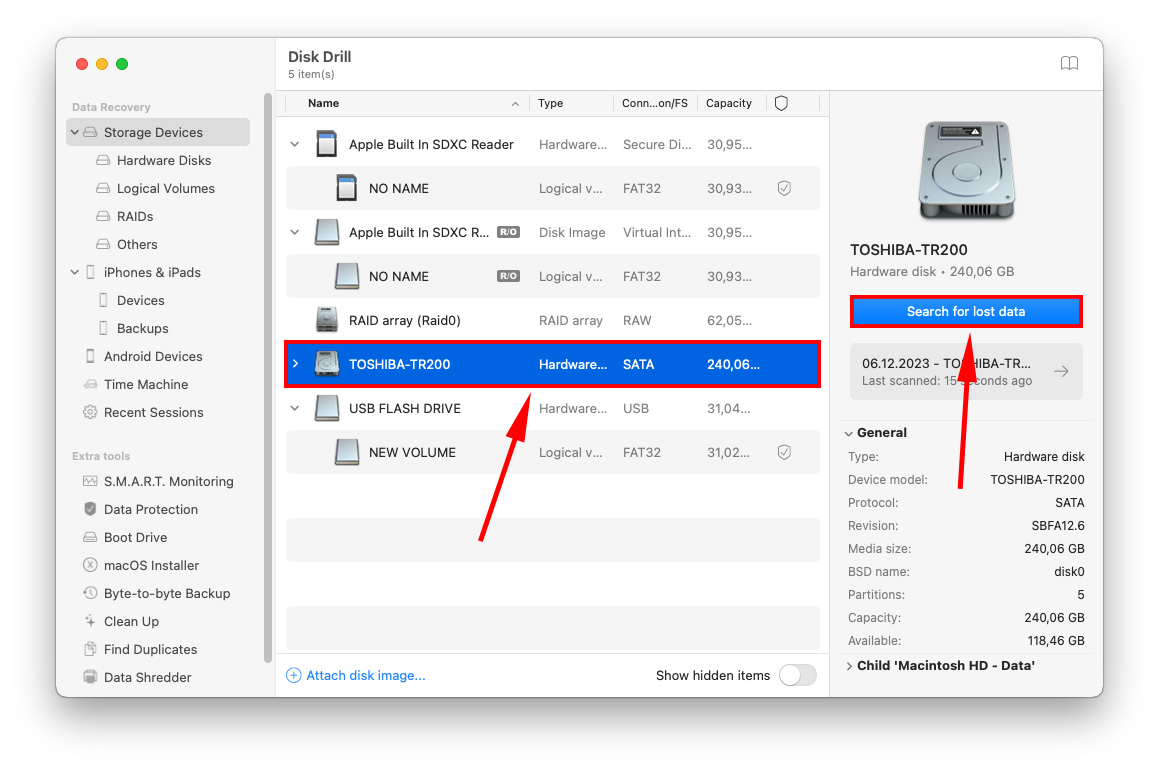
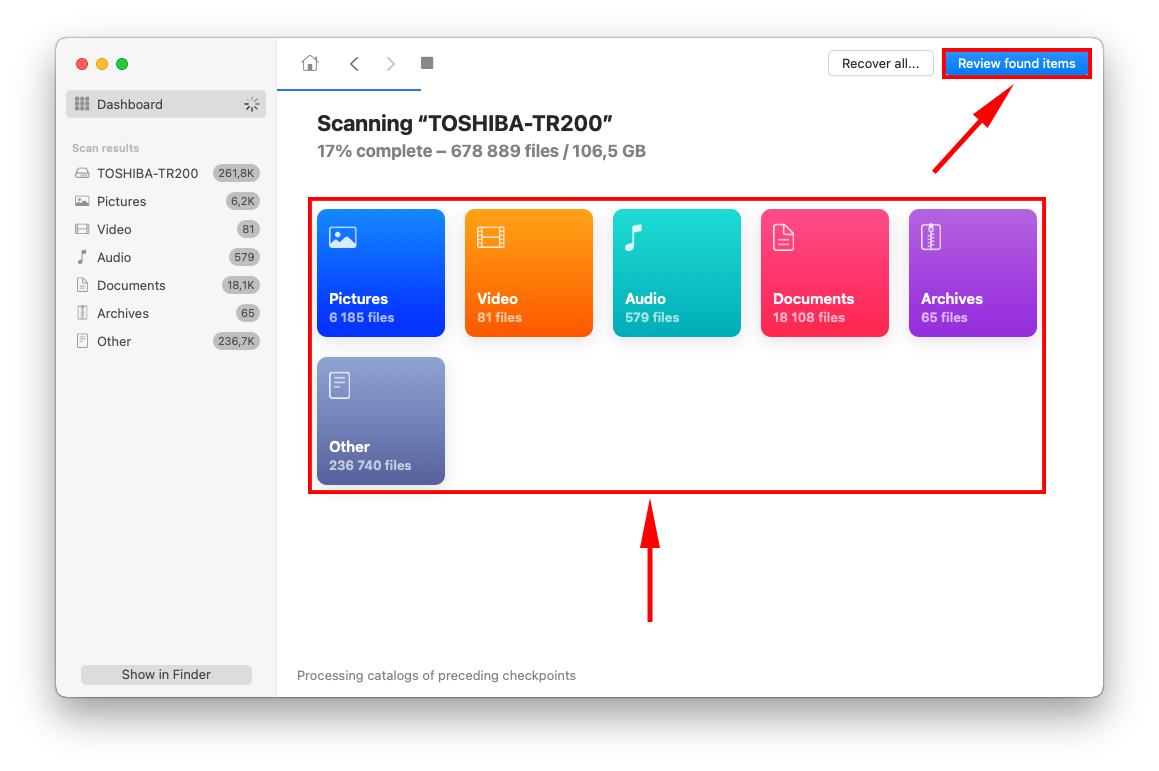
Step 5. Even if Disk Drill hasn’t completed its scan, you can start browsing through found data by clicking one of the file type boxes. Or you can wait for the scanning process to complete then click Review found items.
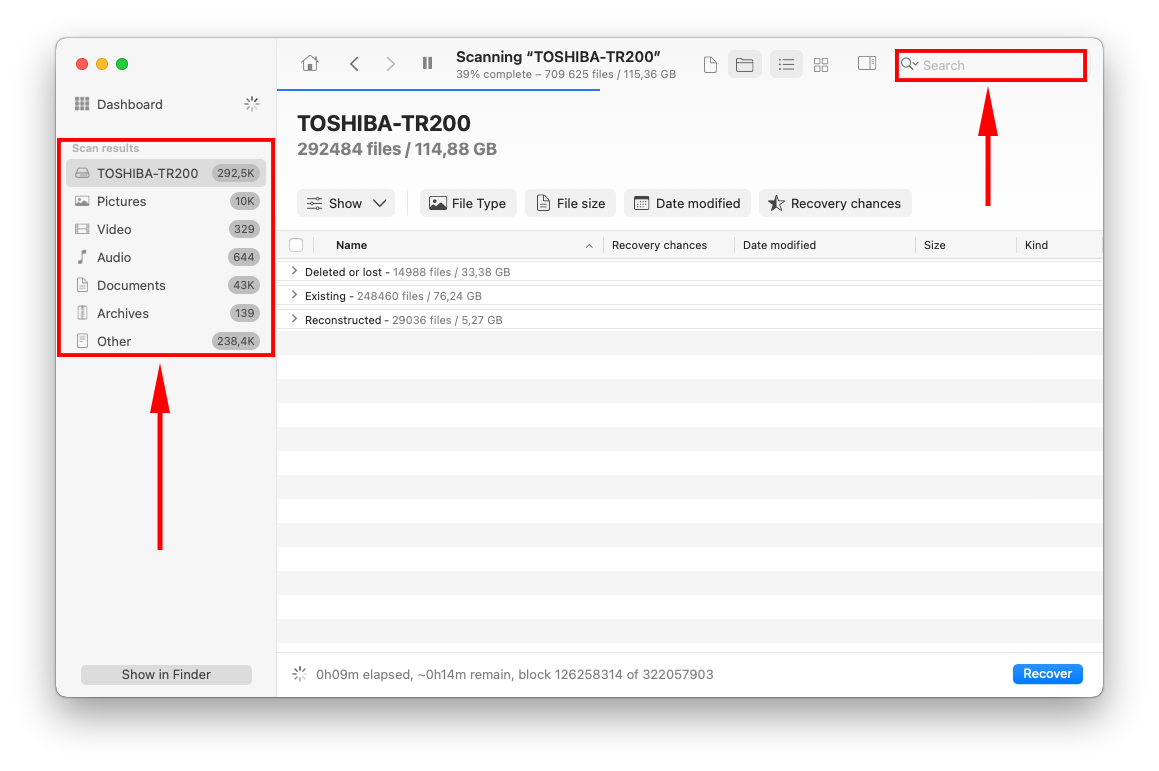
Step 6. You’ll be greeted by a list of found data that continues to populate until the scan completes. You can browse through the results manually or you can narrow your search by using the search bar on the top right corner of the window, or by using the file type selection sidebar on the left.
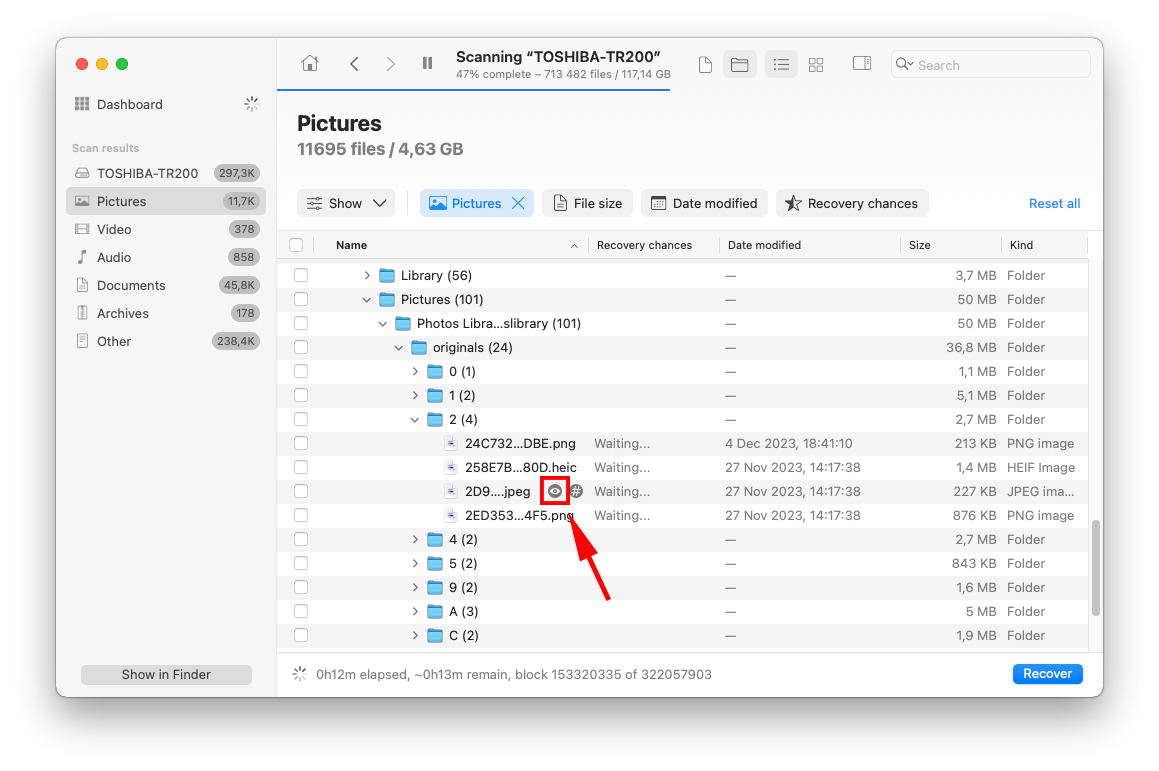
Step 7. You can preview any file by hovering your mouse pointer beside the file name and clicking the eye button that appears.
Step 8. To select the files you want to recover, tick the checkboxes to the left of the file names. Finally, click Recover.
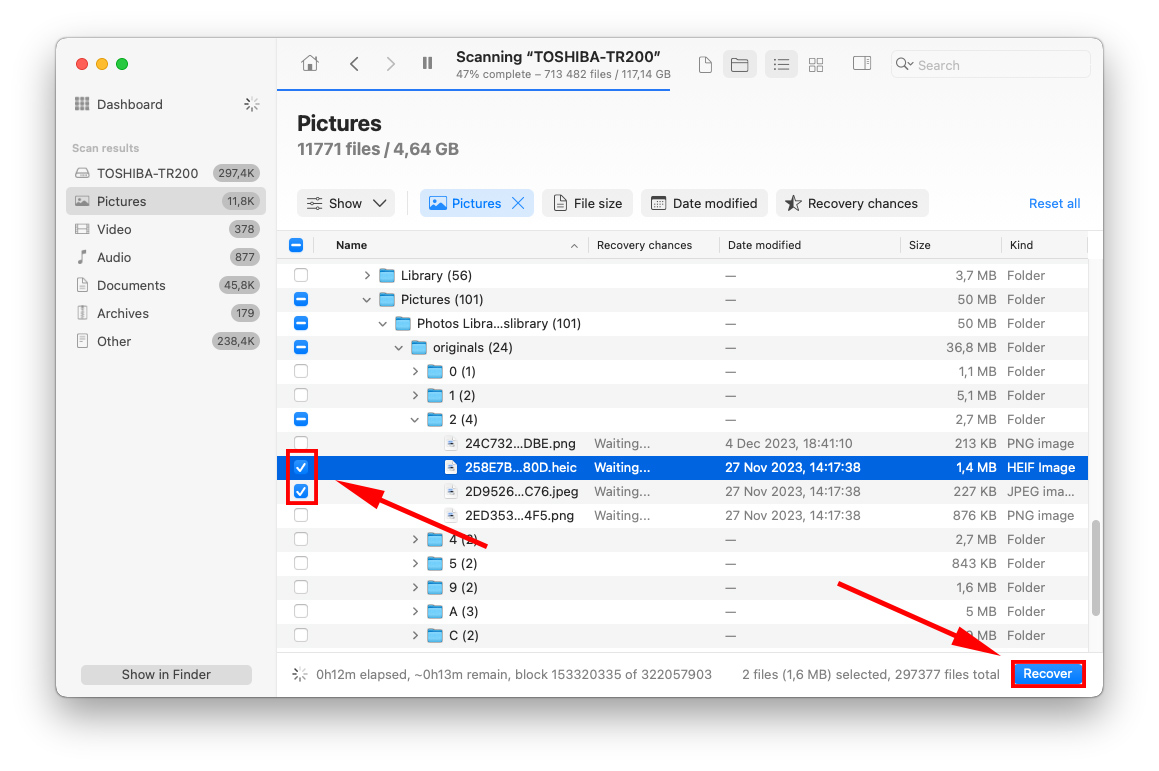
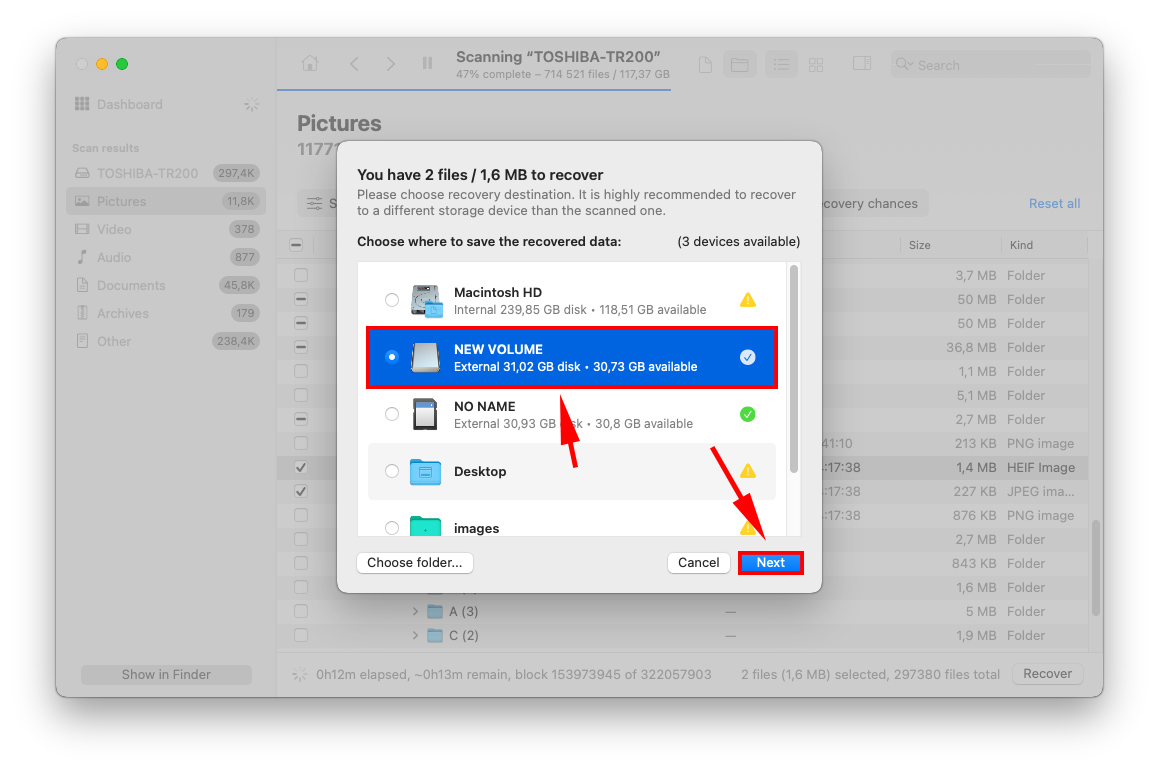
Step 9. On the dialogue box that appears, use the dropdown menu to choose where you want to save your files. It’s always a good idea to save them to another storage device if you think the drive you’re scanning is corrupted.
Method 3: Check the Recently Deleted Album on Your Photos App
Whenever you delete a photo, it’s automatically sent to the Recently Deleted album in your Photos app. It stays there for 30 days by default and automatically erased (permanently) after that duration.
Photos in the Recently Deleted album don’t show up during searches, so it’s worth checking here if the other methods didn’t work for you, even if you don’t remember deleting your photos.
To check the Recently Deleted album in the Photos app, open the Photos app and click Recently Deleted in the left sidebar. If you find your photos, click on them to select them and click Restore. They’ll be returned to their old location.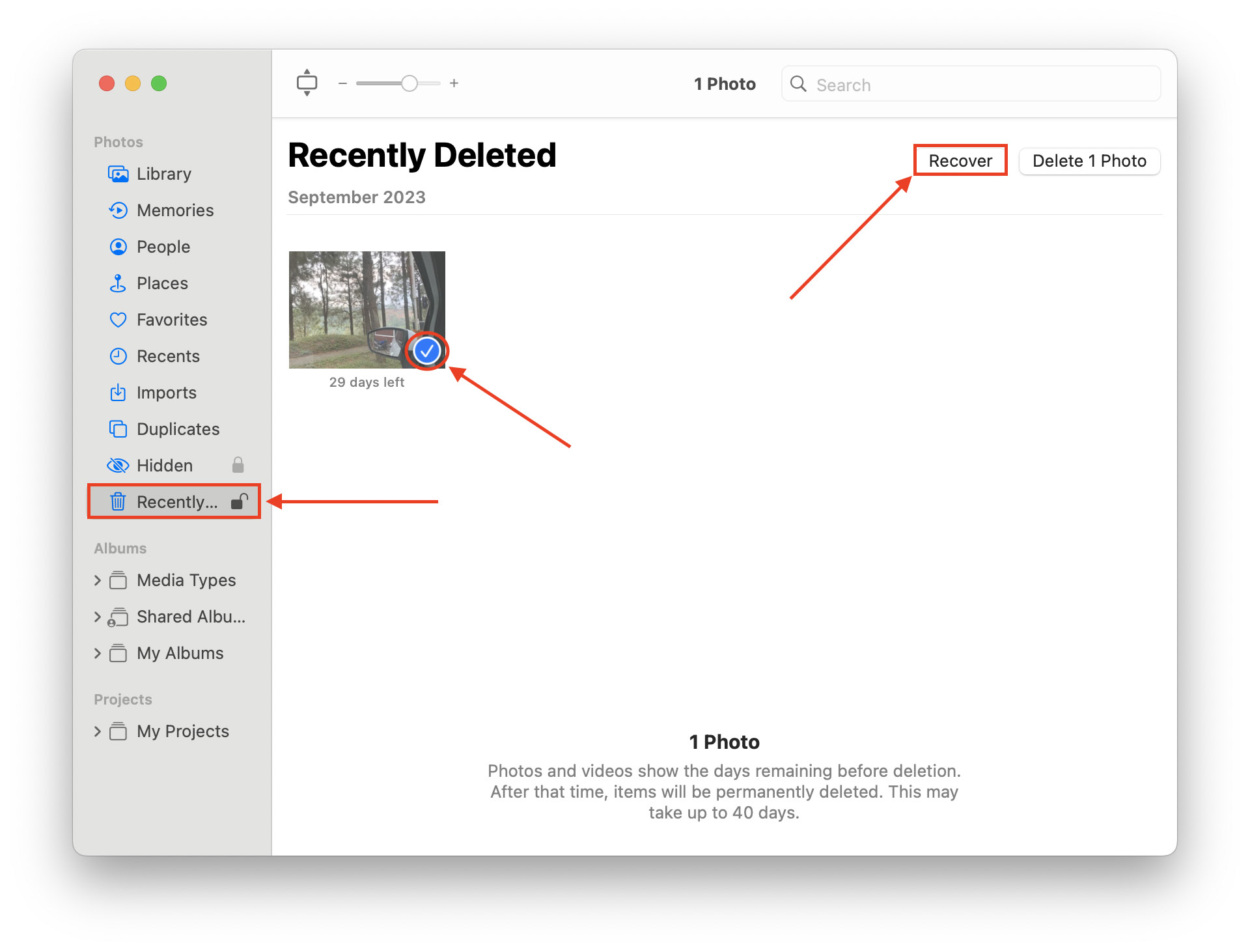
Method 4: Check the Recently Deleted Album on iCloud
If you have iCloud enabled for your Photos (or you uploaded your photos and managed them there), try checking the Recently Deleted album. As with the Photos app, deleted iCloud photos are only kept for 30 days and permanently erased after.
To check the Recently Deleted album on iCloud:
Step 1. Log into iCloud.com and click on the Photos app icon.
Step 2. In the left sidebar, click Recently Deleted. If your photos are here, click on them to select them and click Restore. They should be returned to their last location.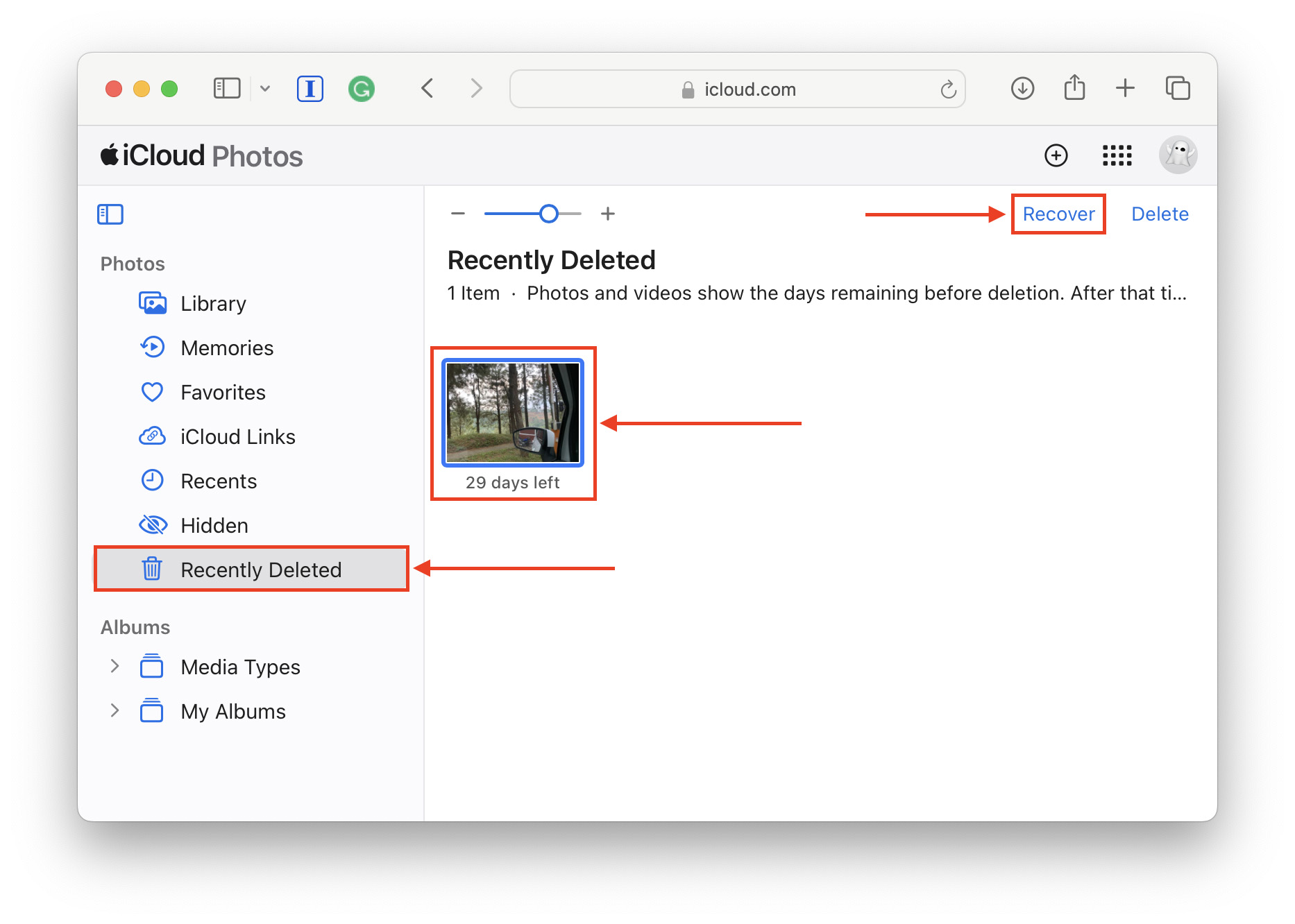
Wait! Do You Have Any Missing?
Have you looked everywhere but still can’t find the folders you’re looking for? If even Spotlight and advanced search can’t find your folders, there’s a chance that you unknowingly deleted them–check out our guide on how to recover deleted folders on your Mac. Just make sure that you rename any existing folders that use the same folder name as the one you’re trying to restore, because it may end up getting overwritten by the recovered folder.






