
If you used the RM command (with or without its extensions) on Mac and deleted files that turned out to be important, you have a limited time frame to recover your data before it’s gone forever. The command is fast and silent, and it completely skips the Trash folder.
In this article are 3 safe methods to recover RM files on Mac, as well as in-depth information about the RM command and the most important factors that affect your chances of recovery. Read on.
Table of Contents
What is RM Command in Mac Terminal
In the context of Unix (Mac) and Linux systems, the RM command is an erase or “remove” tool. It’s handy for users who often work from the Terminal or for quick batch deletion. Depending on how you type it, the RM command can accomplish different things:
| RM Command | Function |
| rm -i | Prompts the user for confirmation before deleting each file. |
| rm -I | Prompts the user for confirmation once before deleting a batch of files. |
| rm -f | Immediately deletes files upon execution without prompting the user for confirmation. |
| rm -r | Deletes directories along with all their content. |
| rm -v | Outputs information about the deleted files as they are being removed. |
| rm -d | Deletes a directory only if it’s empty. |
The RM command is a powerful tool that can help users manage their files more efficiently. But what if a user accidentally used the RM command for files they don’t want to delete? Is it still possible to recover their files? Let’s find out in the next section.
Is it Possible to Undo RM Command on Mac?
The possibility of undoing the RM command’s effects on your Mac and recovering your RM files depends on multiple factors that mainly concern overwriting.
The normal behavior of a traditional hard drive is to continue storing the data of deleted files until they get overwritten. The window of recovery occurs between the time of deletion and overwriting. However, the availability of this window depends on the following:
- Original file location – If your deleted files were originally located in a folder synchronized with iCloud, you can try using the Data Recovery tool in iCloud web.
- What occurred after RM was executed – If you downloaded or transferred any new files to the drive that originally stored your files (after the point of deletion), you may have potentially overwritten any data left over by the deleted files. This makes recovery impossible.
- TRIM on SSD drives – If your Mac uses an SSD instead of a hard drive, TRIM may be enabled. This setting automatically erases data blocks of deleted files instead of waiting for overwriting.
- Available backups: If you created a backup before your files were deleted by the RM command, getting your files back is as easy as restoring that backup.
As long as the files you deleted with the RM command haven’t been overwritten by new data or wiped out by the TRIM function, you have a good chance of recovering them using data recovery software. If you have backups or you enabled iCloud synchronization, your chances of recovery are even better.
How to Recover RM Files on Mac
Due to how powerful the RM command is, to recover deleted files from terminal, you’ll need to either rely on backups or use a third-party tool called data recovery software to extract your files directly from the file system. And as we mentioned earlier in the article, you’ll need to act fast – every minute that passes can eat into your deleted data.
Method 1: Use Data Recovery Software on Your Drive
If you don’t have any backups, the only way to recover deleted files is to use data recovery software. It’s a tool that can scan storage devices for whatever data remains after deleting a file or folder, and use that data to restore your files to a usable state.
There are several data recovery tools you can choose from, but we’ll be using an app called Disk Drill for this guide. It’s the most beginner-friendly recovery software we’ve tested, and it’s compatible with the latest version of macOS. Disk Drill also supports a lot more file formats compared to other recovery software, which makes it a good choice for this scenario.
It also has a very good preview feature, which can display the entirety of your files’ contents–which is also the best way to verify if a file is recoverable. And you can scan your drive and preview your files as much as you want for free; you only need to purchase the one-time license during the actual recovery phase.
Step 1. Download and install Disk Drill on your Mac. However, if the files you deleted with RM were originally stored on your Mac, install Disk Drill on an external storage device (like a USB drive) instead.
Step 2. Run Disk Drill and grant the necessary permissions, as shown by the installer.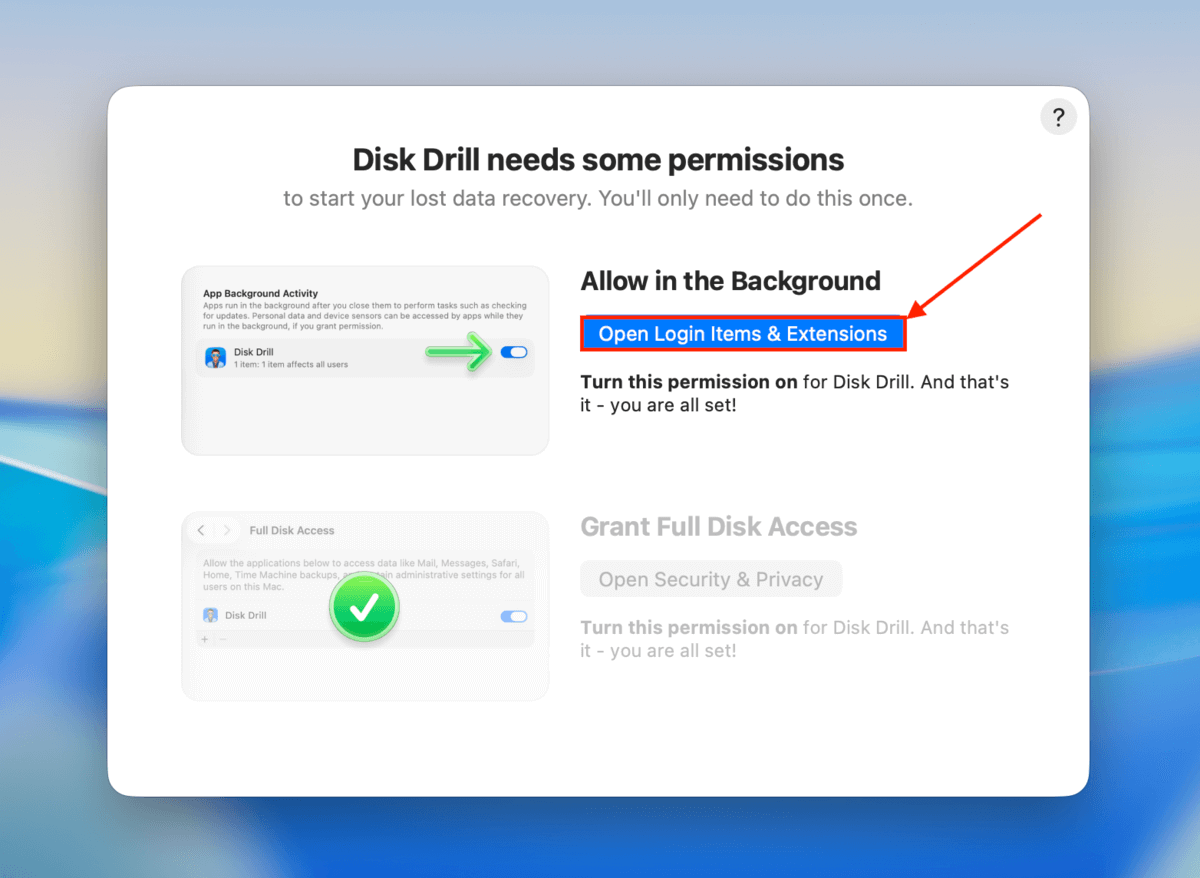
Step 3. Once you get to Disk Drill’s main menu, select the drive your files were stored on (before they were deleted). Then, click Search for lost data. If a prompt appears asking you to choose a scan type, select Universal scan.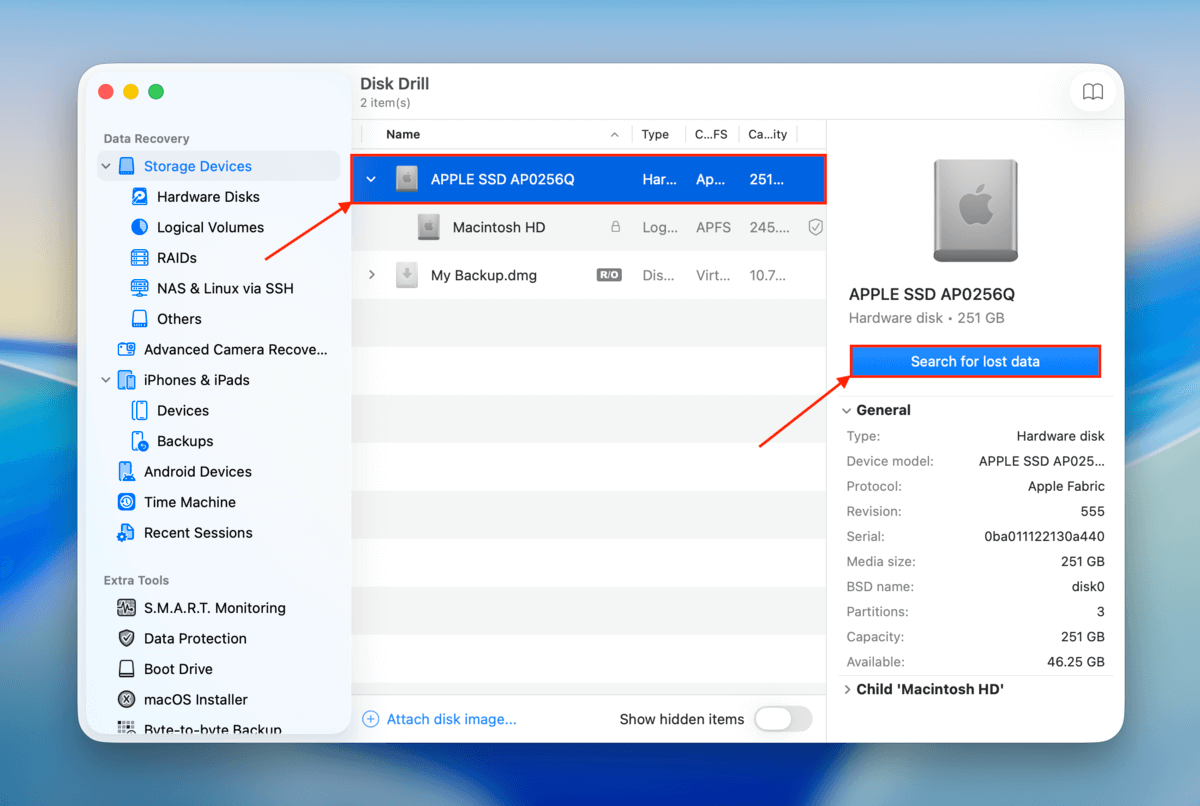
Step 4. Wait for Disk Drill to completely finish scanning your drive for the best results. Then, click Review found items.
Step 5. Use the filters in the left sidebar, as well as the search tool in the top right corner, to quickly narrow down the scan results and find your files more quickly. When you find them, we recommend clicking each file once to preview its contents.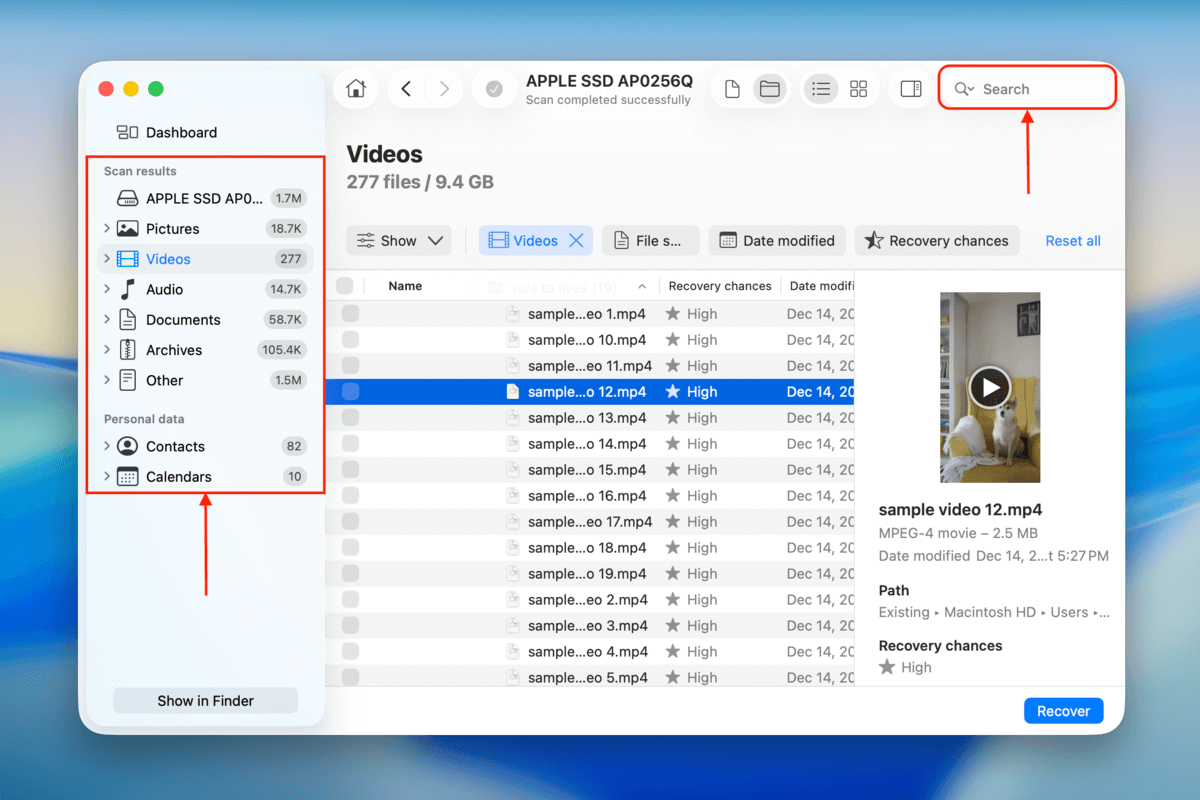
Step 6. Use the checkboxes in the leftmost column to select your deleted files. Then click the Recover button.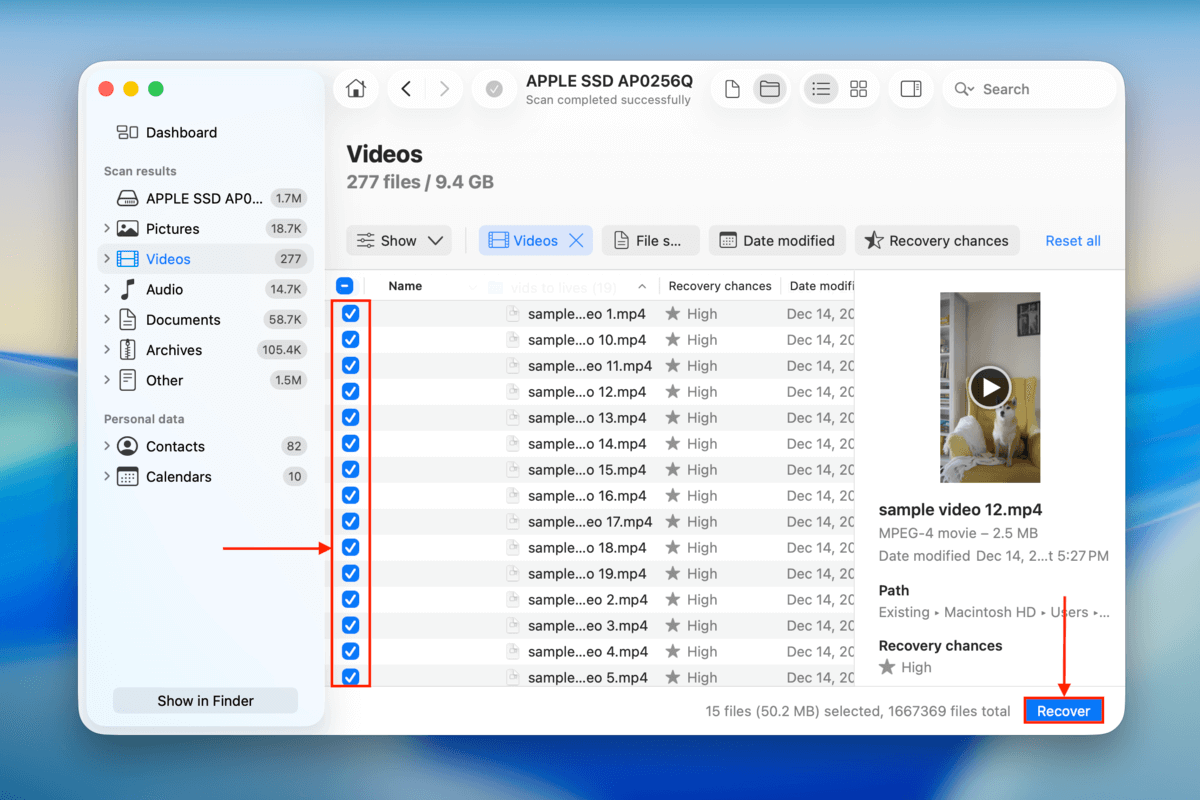
Step 7. In the dialog menu that appears, select a folder where you want Disk Drill to save the restored files. Make sure that you choose a location on a different drive than where your files were originally saved (e.g., if you deleted the files from your Mac, save the recovered data to an external drive). Finally, click Next.
After clicking Next, Disk Drill will immediately begin the recovery process. Your files will appear in the folder you selected in step 8. We recommend that you try opening them and ensuring no errors before you close the Disk Drill app.
Method 2: Utilize iCloud’s Data Recovery Tool
Do you have iCloud synchronization enabled on your Mac? Folders that you allowed to synchronize with iCloud are automatically uploaded to Apple’s servers. If the files you deleted with the RM command were stored in any of these folders, you might be able to use iCloud’s own data recovery tool to restore them. Here’s how to use it:
Step 1. Open a browser on your Mac and navigate to iCloud.com. Then, log in with your account.
Step 2. At the top of the page, click the menu button (beside your profile button). In the context menu that appears, select Data Recovery.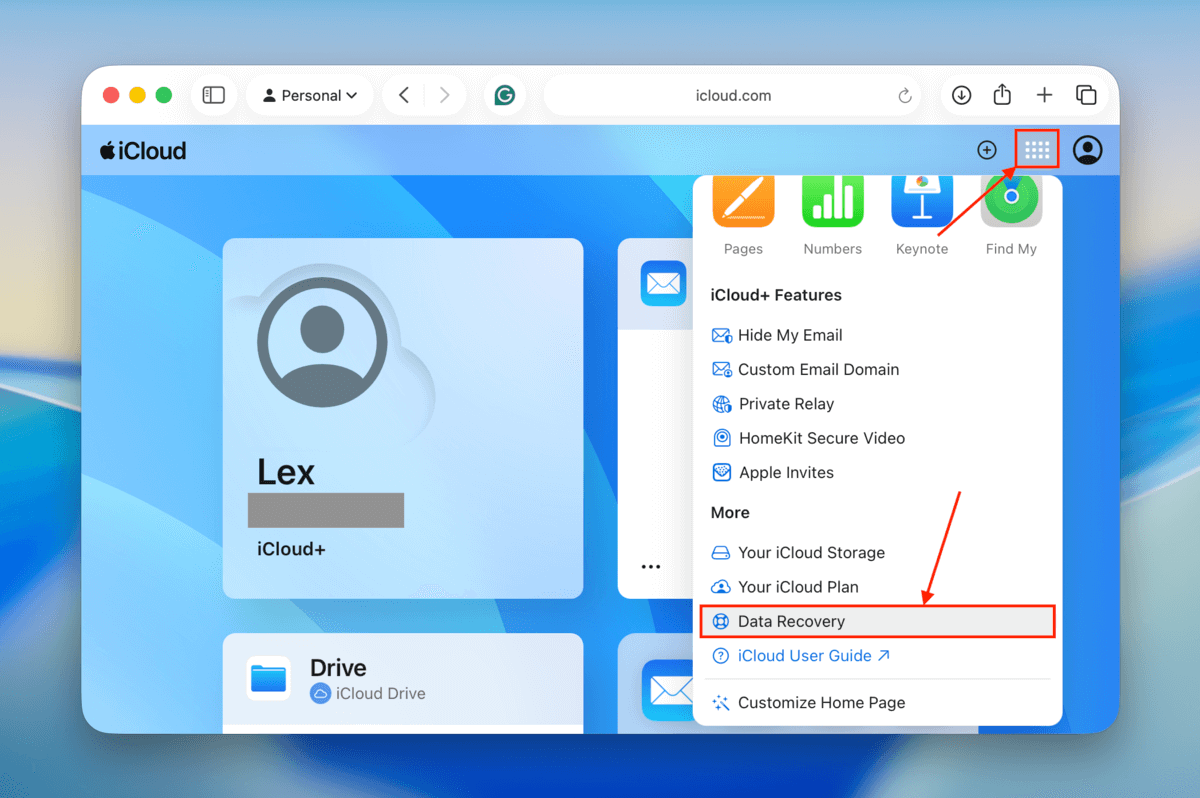
Step 3. Click the Restore Files section.
Step 4. Select the files you want to restore. Alternatively, click the Select All button if you want to recover everything on the list. Then, click the Restore button.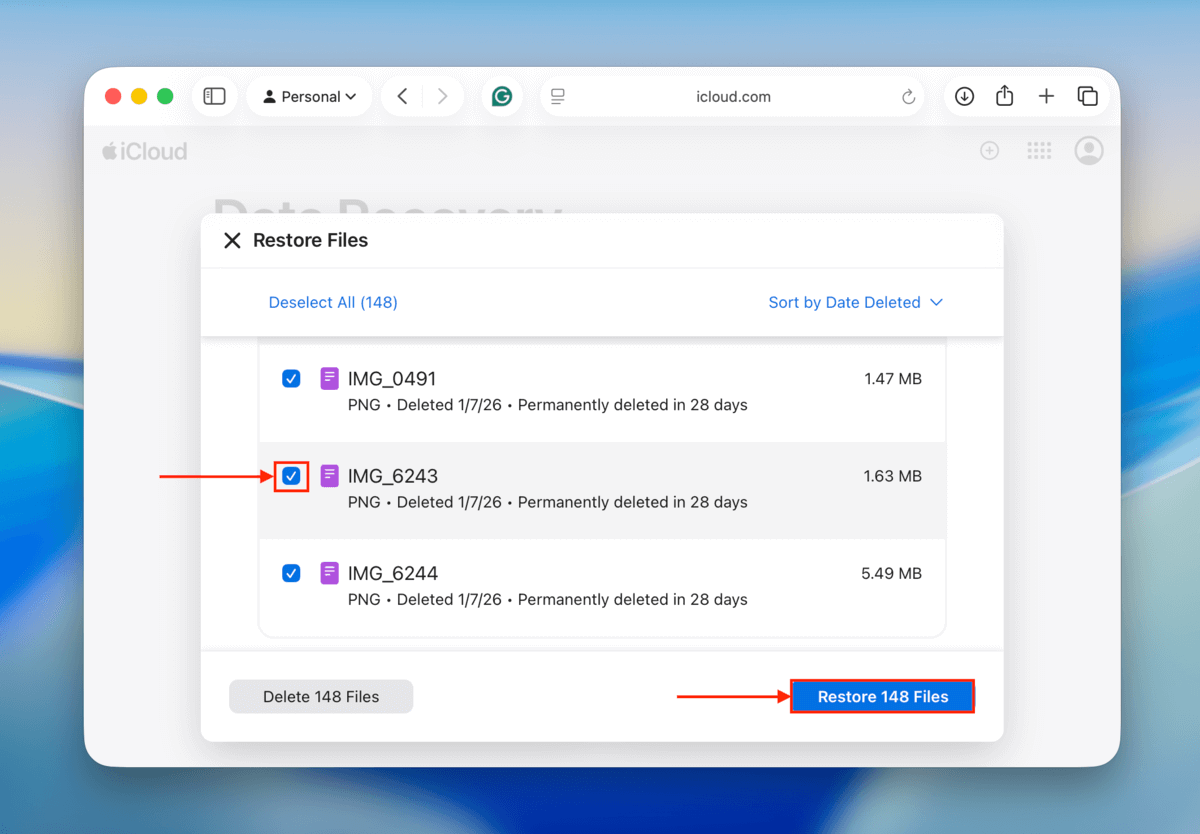
Any files you restore with iCloud’s data recovery tool will be returned to their original locations. Make sure that those locations don’t have existing files with the same names, as they might be overwritten.
Method 3: Restore a Time Machine Backup
Time Machine is a Mac backup utility that saves “snapshots” of your files and folders. If you created a backup before your files were deleted, you can restore their snapshots through Time Machine. This is the most reliable way to recover files that were deleted due to the RM command or any other reason; however, it’s completely reliant on the preventative measures you took beforehand (which is why it’s so low on our list).
Step 1. Connect your Time Machine backup drive to your Mac.
Step 2. On the menu bar, click the Time Machine button. In the menu that appears, select Browse Time Machine backups…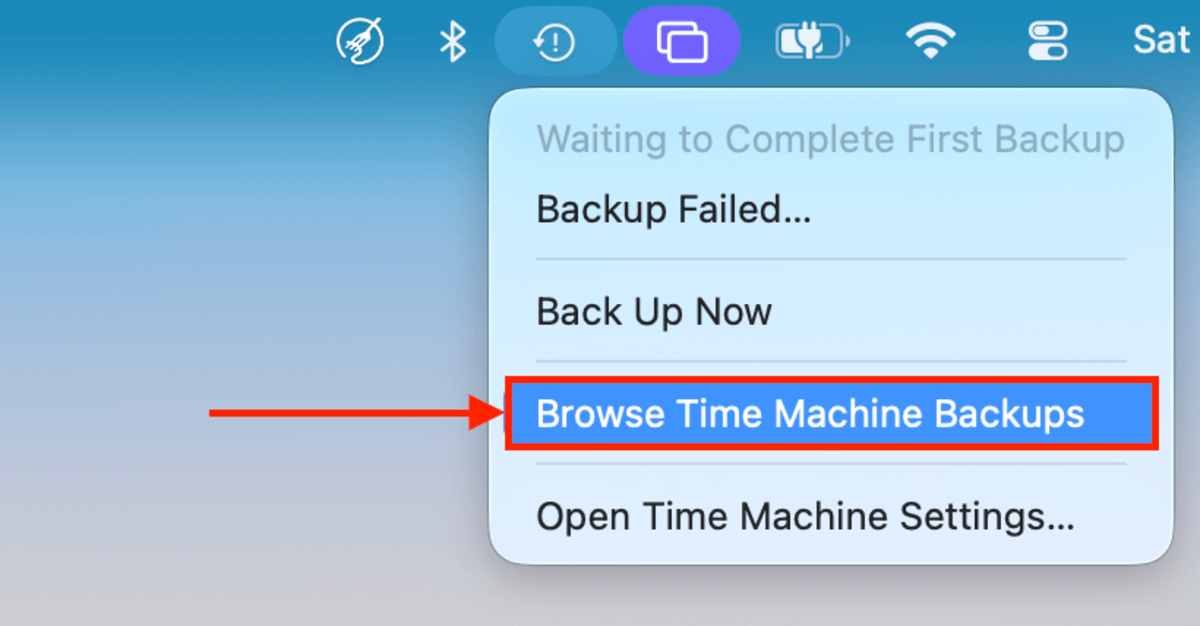
Step 3. In the Finder window in Time Machine, navigate to the location where your files were originally stored (before getting deleted by RM). Then, use the arrow keys on the right to browse earlier snapshots of that folder. Once your deleted files appear, select them and click the Restore button.
Conclusion
The RM command is a powerful command line tool that works fast to erase your files. And once those files get overwritten by new data, even the most powerful data recovery software will struggle to recover them. To avoid unwanted (and permanent) consequences from using the RM command, we suggest creating Time Machine and iCloud Backups regularly.
FAQ
To undo RM’s deletion, try the following methods:
- Restore your data from a Time Machine backup.
- Restore your data using iCloud’s data recovery tool.
- Use data recovery software to restore your data directly from your drive’s file system.






